Deploying To Github Packages Through Azure Devops
With the release of Github’s own package registry there’s now yet another place for developers to source their dependencies. Luckily, integrating this with your existing Azure DevOps workflow is trivially done in just a few steps.
Add the task
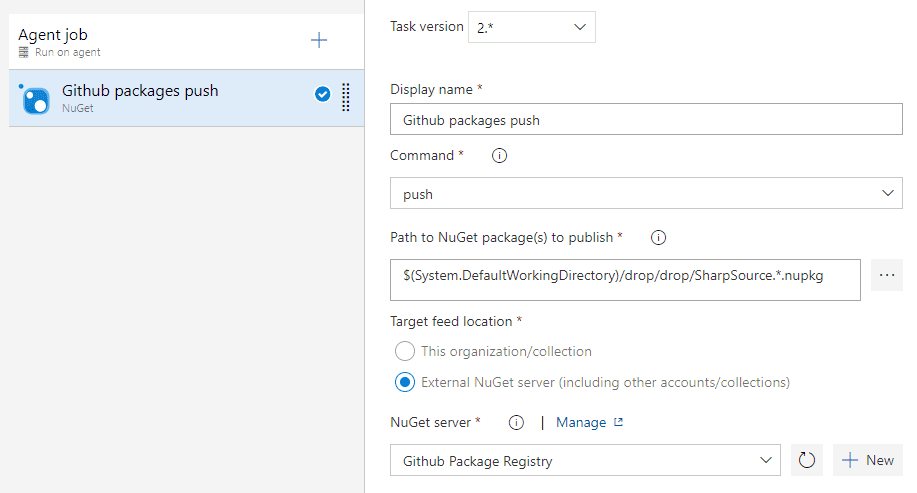
The general setup is the same as any other NuGet step: add a Nuget task using the push command and point it to the nupkg file that your build process generated.
Configure the service connection
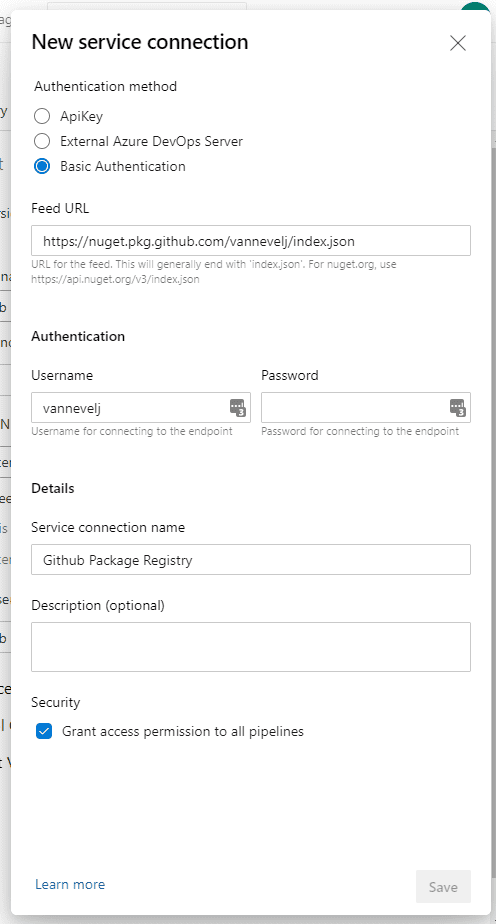
We then create a new service connection for the Github package registry. Reading the Github docs, it appears that only username+password is supported so select Basic Authentication.
The Feed URL is in the form of https://nuget.pkg.github.com/OWNER/index.json where OWNER should be replaced with the user or organization that you’re deploying to (all lowercase!). In my case this becomes https://nuget.pkg.github.com/vannevelj/index.json.
Rather than using your actual password, generate a Personal Access Token on your Github account that has read:packages, write:packages and delete:packages permissions.
Configure the nuget package
At this point the only thing left to do is ensure that our .nuspec file is up to scratch. Most importantly, ensure that the repository property is set as Github uses it to verify the package matches the user/org you’re trying to add it to. When using a .nuspec file, add an entry along the lines of <repository type="git" url="https://github.com/vannevelj/sharpsource'>.
If you instead use csproj properties, the equivalent is <RepositoryUrl>https://github.com/vannevelj/sharpsource</RepositoryUrl>
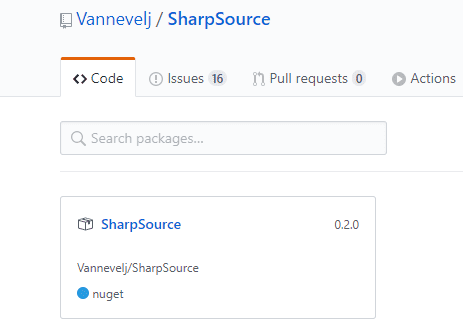
The end result speaks for itself: